
Alice in NonEuclidean Space Time
Euclidean space is the fundamental space of geometry, intended to represent physical space.

Euclidean space Wikipedia Euclidean space, Cartesian coordinates
In Newtonian physics, time is embedded in Euclidean 3-space as a parameter, whereas relativity uses a Lorentz metric (or Minkowski metric) to join time and space into spacetime, a 4-dimensional Minkowski space. This will be covered at some length in section 3.

Euclidean space YouTube
Euclidean space, In geometry, a two- or three-dimensional space in which the axioms and postulates of Euclidean geometry apply; also, a space in any finite number of dimensions, in which points are designated by coordinates (one for each dimension) and the distance between two points is given by a distance formula.

EUCLIDEAN SPACES OF 2, 3, 4, …, n DIMENSIONS Euclidean space, Order
That one chirality of Euclidean space-time rotations appears after analytic continuation to Minkowski space-time as an internal symmetry is the most hard 3. to believe aspect of the proposed framework for a uni ed theory outlined above. One reason for the very long time that has passed since an earlier embryonic
Euclidean Space Vector img
In mathematical physics, Minkowski space (or Minkowski spacetime) ( / mɪŋˈkɔːfski, - ˈkɒf -/ [1]) combines inertial space and time manifolds with a non-inertial reference frame of space and time into a four-dimensional model relating a position ( inertial frame of reference) to the field.
Euclidean Space by PomPrint on DeviantArt
An event in spacetime has four coordinates, three in space and one in time: (t,x,y,z). However, spacetime plots are usually simplified by using only two axes: The vertical axis is time and the horizontal axis is space, as shown in Figure 9.9. We ignore the other two dimensions of space for the sake of convenience.
1.1. Euclidean Space 1 Impelluso © 2022 EUCLIDEAN SPACE AND NEWTONIAN
In 1906 Poincaré showed that the Lorentz transformation can be regarded as a rotation in a 4-dimensional Euclidean space-time introduced by adding an imaginary fourth space-time coordinate \(ict\) to the three real spatial coordinates. In 1908 Minkowski reformulated Einstein's Special Theory of Relativity in this 4-dimensional Euclidean.

Euclidean Space YouTube
The Large Scale Structure of Space-Time is a 1973 treatise on the theoretical physics of spacetime by the physicist Stephen Hawking and the mathematician George Ellis.. presented in an almost Euclidean fashion, though he acknowledged that this is not a textbook due to its lack of examples and exercises. He praised its 62 illustrative diagrams.

A replica wormhole spacetime that contributes in to the Euclidean path
Abstract We consider a SO(d) gauge theory in an Euclidean d-dimensional space-time, which is known to be renormalizable to all orders in perturbation theory for 2 d 4. Then, with the help of a space-time representation of the gauge group, the gauge theory is ≤ ≤ mapped into a curved space-time with linear connection.

Spherical spacetime time is a fourdimensional continuum of space and
The revolution experienced by modern physics began to be reflected in the 12th edition (1922) of the Encyclopædia Britannica with Sir James Jeans 's article "Relativity.". In the 13th edition (1926) a wholly new topic, "Space-Time," was discussed by the person most qualified in all the world to do so, Albert Einstein.

The Impossible Is Possible! Squaring the Circle and Doubling the Cube
A Euclidean space is a real vector space V and a symmetric bilinear form ·, · such that ·, · is positive defnite. Analogously, a Hermitian space is a complex vector space V and a Hermitian form ·, · such. From last time, we saw that for any pairing, there exists an orthogonal basis where all of the self-pairings were either 1, 0, or 1.
An embedding diagram in Euclidean space of a Schwarzschild spacetime
> The only known non-perturbative definition of Yang-Mills theory is in Euclidean space-time. What is the definition of Yang-Mills theory in Euclidean space-time that you're referring to? Peter Woit says: April 6, 2022 at 10:45 am Prof. Legolasov, The lattice gauge theory definition. This very much requires Euclidean signature to make sense.
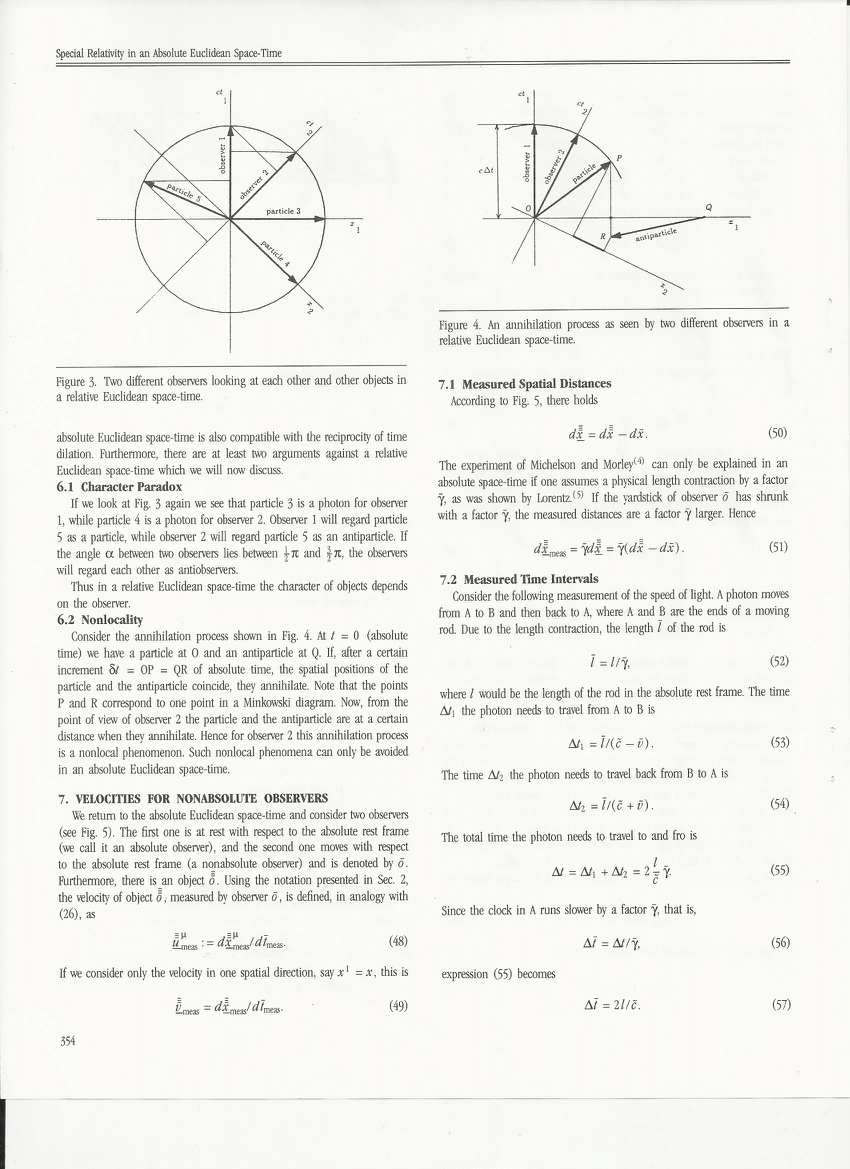
(PDF) Special Relativity in an Absolute Euclidean SpaceTime
Euclidean relativity proposes a circular geometry as alternative that uses proper time as the fourth spatial dimension. Other common elements in Euclidean relativity are the Euclidean ( ++++) metric as opposed to the traditional Minkowski ( +---) or ( -+++) metric, and the universal velocity c for all objects in 4D space-time.

Euclidean Space YouTube
Euclidean n-space, sometimes called Cartesian space or simply n-space, is the space of all n-tuples of real numbers, (x_1, x_2,., x_n). Such n-tuples are sometimes called points, although other nomenclature may be used (see below). The totality of n-space is commonly denoted R^n, although older literature uses the symbol E^n (or actually, its non-doublestruck variant E^n; O'Neill 1966, p. 3).
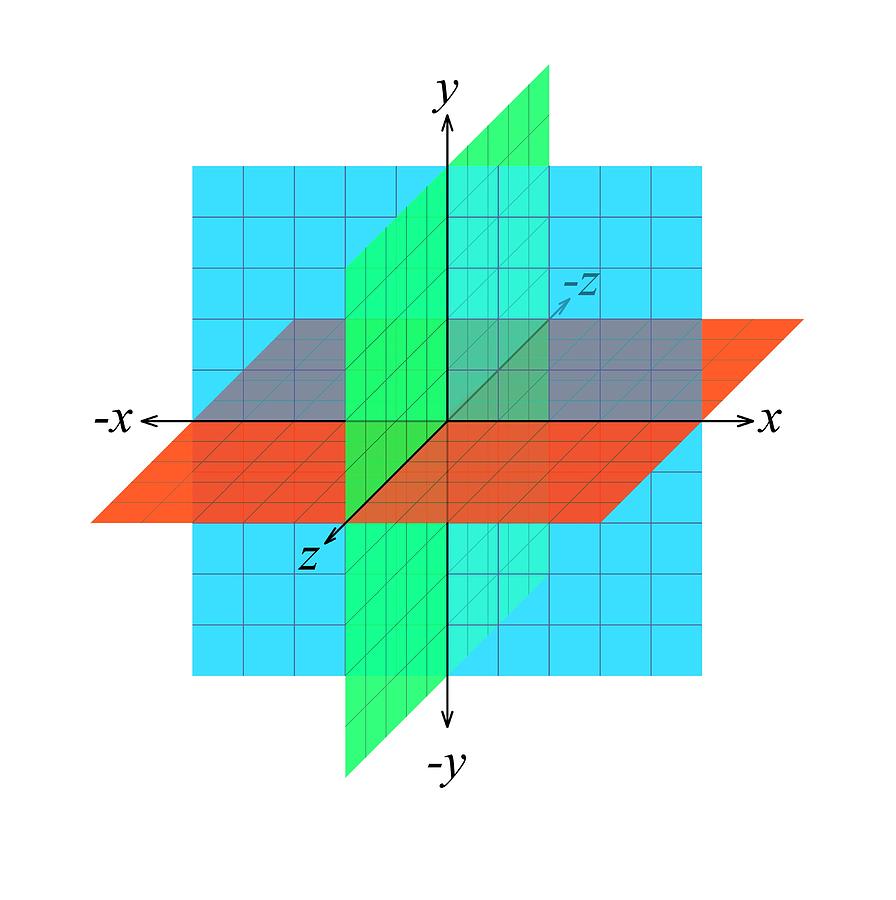
Threedimensional Euclidean Space Photograph by Science Photo Library
Abstract We consider a SO(d) gauge theory in an Euclidean d-dimensional space-time, which is known to be renormalizable to all orders in perturbation theory for 2 d 4. Then, with the help of a space-time representation of the gauge group, the gauge theory is mapped into a curved ≤ ≤ space-time with linear connection.

ANTHROPIA Lost in Time and Space (NonEuclidean Spaces) ft. Arjen A
In cosmology Derivation In the Minkowski spacetime model adopted by the theory of relativity, spacetime is represented as a four-dimensional surface or manifold. Its four-dimensional equivalent of a distance in three-dimensional space is called an interval.